medial meniscus tear diagnostic test|medial meniscus physical exam : online sales There are no risks to your knee from your provider performing a McMurray test. You might feel a little pain or discomfort during the test, but even if your meniscus . See more Notre sélection comprend des lames de terrasse en pin autoclavé, idéales pour les budgets serrés, ainsi que des options plus haut de gamme en bois exotique comme l'ipé ou le cumaru.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Wash exterior of sterilizer according to your facility’s procedure for clinical contact surfaces. Use only quaternary disinfectants to disinfect unit. See User Guide for more information. Examine .
The McMurray test is a series of movements to check your symptoms and range of motion (how far you can move your knee joint). The test is simple and includes the following steps: 1. You’ll lay on your back. 2. Your provider will bend your knee to 90 degrees perpendicular to the rest of your body (about where it . See more
You don’t need to do anything to prepare for a McMurray test. Just visit your provider as soon as possible if you’ve injured your knee or you notice any new . See moreTry to relax while your provider is moving your leg and knee during a McMurray test. Because the McMurray test is a series of physical motions, make sure . See moreA McMurray test is usually a first step in treating your knee. If your provider feels or hears anything in your knee during a McMurray test, they’ll recommend either . See moreThere are no risks to your knee from your provider performing a McMurray test. You might feel a little pain or discomfort during the test, but even if your meniscus . See more
McMurray's test is used to determine the presence of a meniscal tear within the knee. Technique. Patient Position: Supine lying with knee completely flexed. Therapist Position: on the side to .The McMurray test is a series of knee and leg movements healthcare providers use to diagnose a torn meniscus. It’s an in-office physical exam, which means your provider can perform it without any special equipment or a separate appointment.McMurray's test is used to determine the presence of a meniscal tear within the knee. Technique. Patient Position: Supine lying with knee completely flexed. Therapist Position: on the side to be tested. Proximal Hand: holds the knee and palpates .
squat test for meniscus tear
But X-rays can help rule out other problems with the knee that cause similar symptoms. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). This uses a strong magnetic field to produce detailed images of both hard and soft tissues within your knee. It's the best imaging study to detect a torn meniscus. Ege's test helps diagnose a meniscus tear in the knee. It involves putting weight on the knee in a squatting position under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Pain or a clicking noise may indicate a meniscus tear. Introduction. The lateral and medial menisci are crescent-shaped fibrocartilaginous structures that collectively cover approximately 70% of the articular surface of the tibial plateau and primarily function in load transmission and shock absorption through the tibiofemoral joint. Meniscal tears are common sports-related injuries in young athletes and can also present as a degenerative condition in older patients. Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with joint line tenderness and a positive McMurray's test, and can be confirmed with MRI studies.
Meniscal injuries can occur in isolation or in association with collateral or cruciate ligament tears. (See "Medial (tibial) collateral ligament injury of the knee" and "Anterior cruciate ligament injury".) The diagnosis and treatment of meniscal injuries will be reviewed here.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans. An MRI scan assesses the soft tissues in your knee joint, including the menisci, cartilage, tendons, and ligaments. MRI is the preferred method of diagnosing acute meniscus tears (tears that occur due . Meniscus Tear Diagnosis. To diagnose a meniscus tear, your doctor will give you a thorough exam and ask how you got your injury. They'll check your knee to see if there's any tenderness.The medial meniscus sits on the inside of the knee and the lateral meniscus sits on the outside of the knee. Meniscus tears usually take place when an athlete twists or turns their upper leg while their foot is planted and their knee is bent. Occasionally menisci can develop as a block or disk shape, which is called a discoid meniscus.The McMurray test is a series of knee and leg movements healthcare providers use to diagnose a torn meniscus. It’s an in-office physical exam, which means your provider can perform it without any special equipment or a separate appointment.
McMurray's test is used to determine the presence of a meniscal tear within the knee. Technique. Patient Position: Supine lying with knee completely flexed. Therapist Position: on the side to be tested. Proximal Hand: holds the knee and palpates . But X-rays can help rule out other problems with the knee that cause similar symptoms. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). This uses a strong magnetic field to produce detailed images of both hard and soft tissues within your knee. It's the best imaging study to detect a torn meniscus. Ege's test helps diagnose a meniscus tear in the knee. It involves putting weight on the knee in a squatting position under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Pain or a clicking noise may indicate a meniscus tear.
Introduction. The lateral and medial menisci are crescent-shaped fibrocartilaginous structures that collectively cover approximately 70% of the articular surface of the tibial plateau and primarily function in load transmission and shock absorption through the tibiofemoral joint. Meniscal tears are common sports-related injuries in young athletes and can also present as a degenerative condition in older patients. Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with joint line tenderness and a positive McMurray's test, and can be confirmed with MRI studies. Meniscal injuries can occur in isolation or in association with collateral or cruciate ligament tears. (See "Medial (tibial) collateral ligament injury of the knee" and "Anterior cruciate ligament injury".) The diagnosis and treatment of meniscal injuries will be reviewed here.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans. An MRI scan assesses the soft tissues in your knee joint, including the menisci, cartilage, tendons, and ligaments. MRI is the preferred method of diagnosing acute meniscus tears (tears that occur due . Meniscus Tear Diagnosis. To diagnose a meniscus tear, your doctor will give you a thorough exam and ask how you got your injury. They'll check your knee to see if there's any tenderness.
special tests for meniscus tear
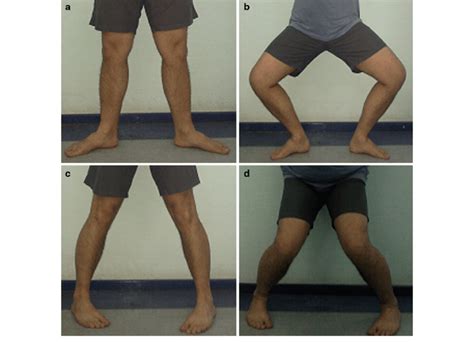
meniscus tear exam findings
l-spreader pasteur pipette quorum testing
The Systec V-Series of top-loading vertical autoclaves in 8 different sizes with 40 to 150 liters chamber volume is distinguished by its small footprint and high chamber capacity. Result: optimal loading capacity with most standard media .
medial meniscus tear diagnostic test|medial meniscus physical exam